Constructing a 12V DC Switch Mode Power Supply
In recent years, the use of switch mode power supply (SMPS) has become more common as more applications demand for greater power efficiency. It uses semiconductor (mostly MOSFET) fast switches to switch DC input that has been rectified at high frequency. The advantages of high frequency switching are that it reduces the size of inductor, capacitors and transformer used. Other advantages of switching power supply over linear power supply are :
a) High Efficiency (up to 90% and above for good design).
b) Output can be higher than input.
c) Able to operate over a wide range of input power supply.
d) Able to have more than one output.
The setback of using SMPS compared to linear power supply is that it generates electrical noise which contributes to electromagnetic compatibility design issues and more component count.
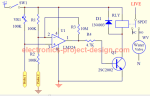
Buck Converter SMPS
The SMPS circuit below from Power Integration uses LNK304 as its high frequency switch. Take note that this circuit is non isolated type which means that the output is not electrically isolated from the input and all testing should be done using an isolation transformer to provide the AC line input to the board.
Make sure that you have electrical safety knowledge and experience before you embark on doing this project.
The features of this project is as summarized below.
Input : 85-265 VAC
Output : 12 V, 120 mA, 1.44 Watt
Low Cost : Only 16 components are needed
No-load power consumption : < 0.2 Watt
Full detailed writeout of schematic design, parts list, printed circuit layout and performance data can be downloaded from Power Integration.
Power Integrations Switch Mode Power Supply


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave us a comment in the box below.