Microcontroller Application Circuit
Reset IC in Microcontroller Application Circuitry
In the design of microcontroller based electronics project, the use of Reset IC is critical for highly critical applications that need to ensure that the MCU will only operate at its optimum voltage. Without the use of reset circuitry, the MCU may go into a tristate of which it may go into abnormal operation.
One example of the use of the Reset IC is that when the input voltage drops below a fixed threshold, the reset IC will assert a reset signal for a fixed period of time after Vcc rises above the fixed threshold value. An example of how a reset circuit is connected is as shown below.
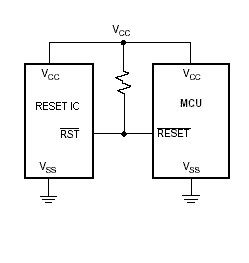
During power up, once Vcc exceeds the reset threshold, the reset line will be kept low for a period after which the line will be pulled high. This resets the MCU after which it will go into normal operation.
If the Vcc drops below the reset threshold, the reset pin will go low. It will stay low for at least the reset time out period and go back to high again.
This operation will ensure that the MCU power supply is monitored and will only go into operation when the Vcc is within the range of its operation. The threshold voltage of the IC is chosen based on the minimum Vcc of the MCU. MCU supply can range from 1.8V to 5.0V and a suitable IC can be chosen to monitor the supply voltage to the MCU. A typical range of RESET IC from ST range from 2.6V to 4.6V.
With the development of lower voltage integrated circuits, there are also reset ICs that can cater for 1.5 V - 3.0 V applications as well.
Back to Microcontroller Application Reset IC Home Page


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave us a comment in the box below.